What's the difference between AC and DC
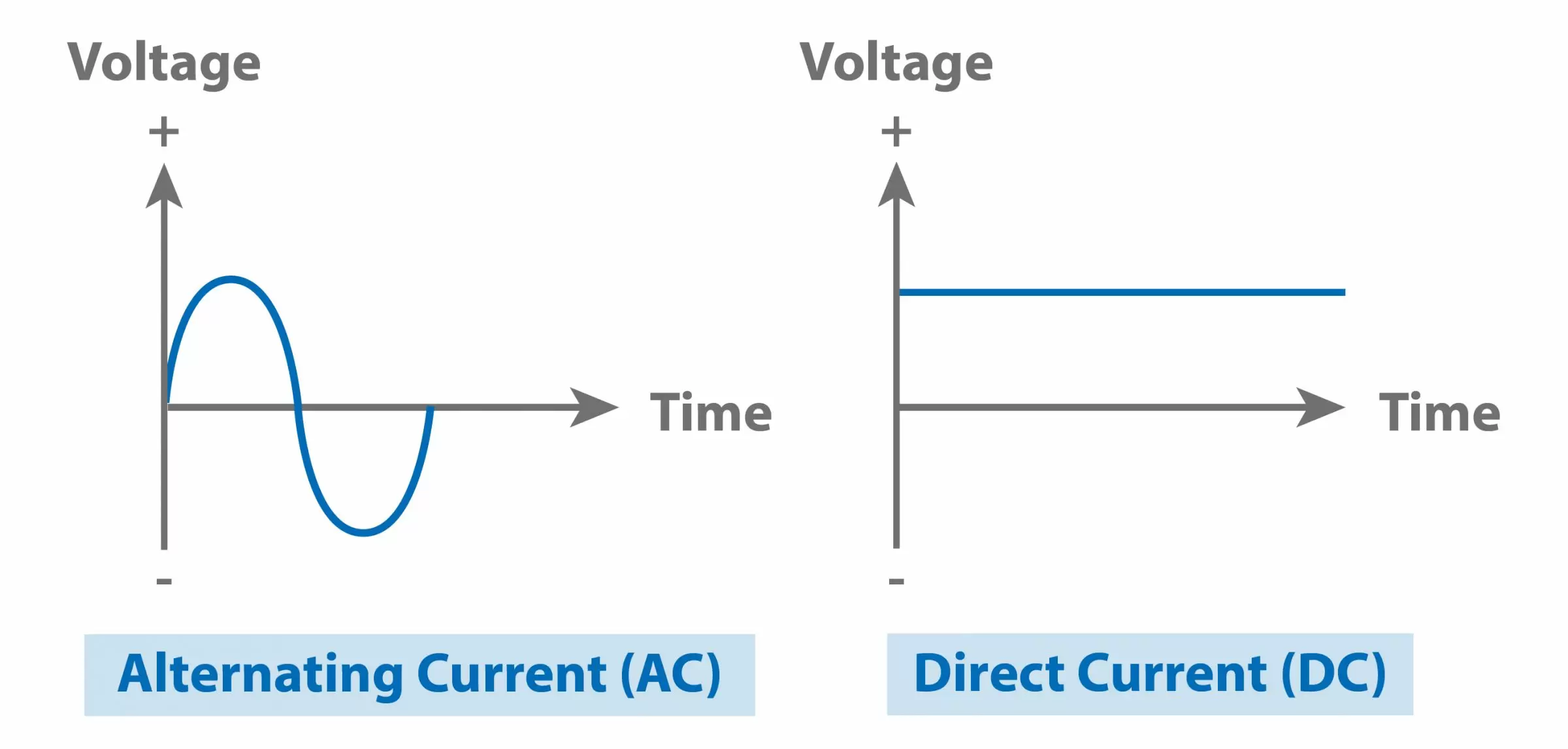
AC stands for "alternating current" and DC stands for "direct current."
The main difference between AC and DC is the direction in which the electric charge flows. In DC, the electric charge flows in one direction, from the positive to the negative terminal of a battery or power supply. In AC, the direction of the electric charge reverses periodically, oscillating back and forth between the positive and negative terminals of a power source.
Another important difference between AC and DC is that AC can be easily transformed into different voltage levels using transformers, while DC cannot. This makes AC more suitable for long-distance power transmission, as it can be transmitted at high voltage levels and then stepped down to lower voltage levels for use in homes and businesses. DC, on the other hand, is more suitable for some types of electronic devices that require a steady and stable power supply.
Finally, AC can be generated more efficiently and at lower cost than DC, which is another reason why it is used for power distribution in electrical grids around the world.