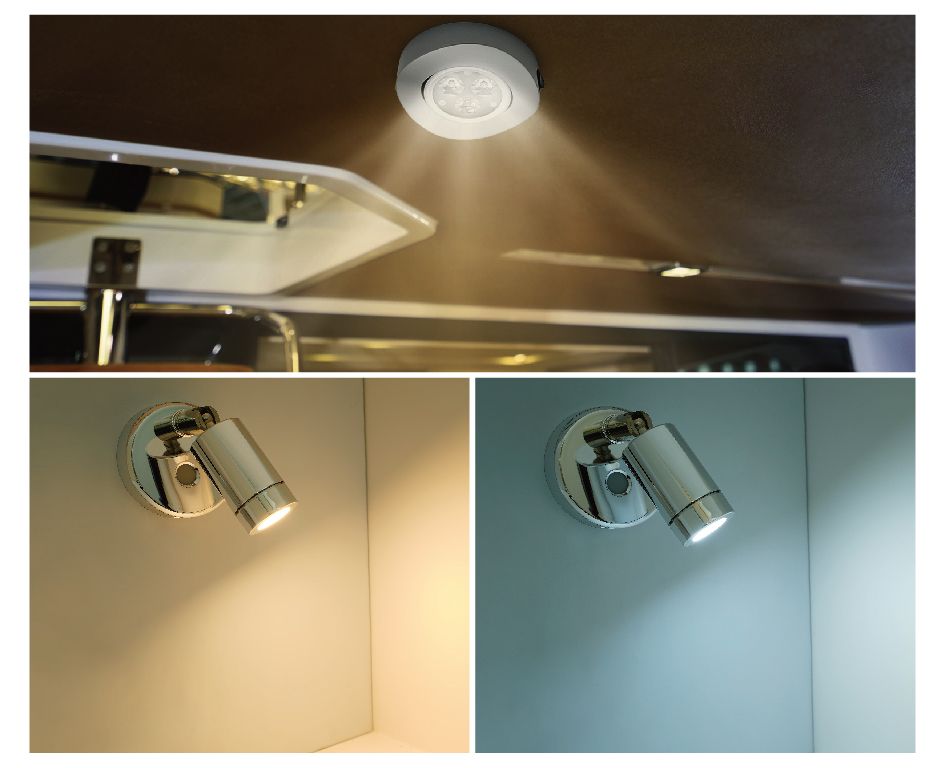
Introduction to LED Terminologies – Color Temperature, Luminous Flux (Lumens), Illuminance (Lux) and LED types
LED is the next generation of lighting. With its lower power consumption, no heat radiation and better durability comparing to traditional halogen lights, the LED lights are an ideal solution on the board. Here is some of the important terminologies of LED lights you need to know before making decisions of LED lights purchases:
Color Temperature (Unit: K (Kelvin))
Color temperature is conventionally stated in Kelvin (K), the unit of absolute temperature. The color temperature is the temperature that makes an ideal black body radiator radiate comparable hue as the light source. Usually, color temperatures over 5,200K are called cool colors, color temperature below 3500K are called warm colors. Warm white LED colors provides more cozy and relax atmosphere and are typically used for living and bed rooms while cool white LED lights set more focus and serious tones for working spaces like engine room and pilot’s cockpit. Recently more and more lights have designed with dual color temperature (warm and cool white) so end users and choose the right color temperature (3000K, 4000K or 6000K) whenever they need it.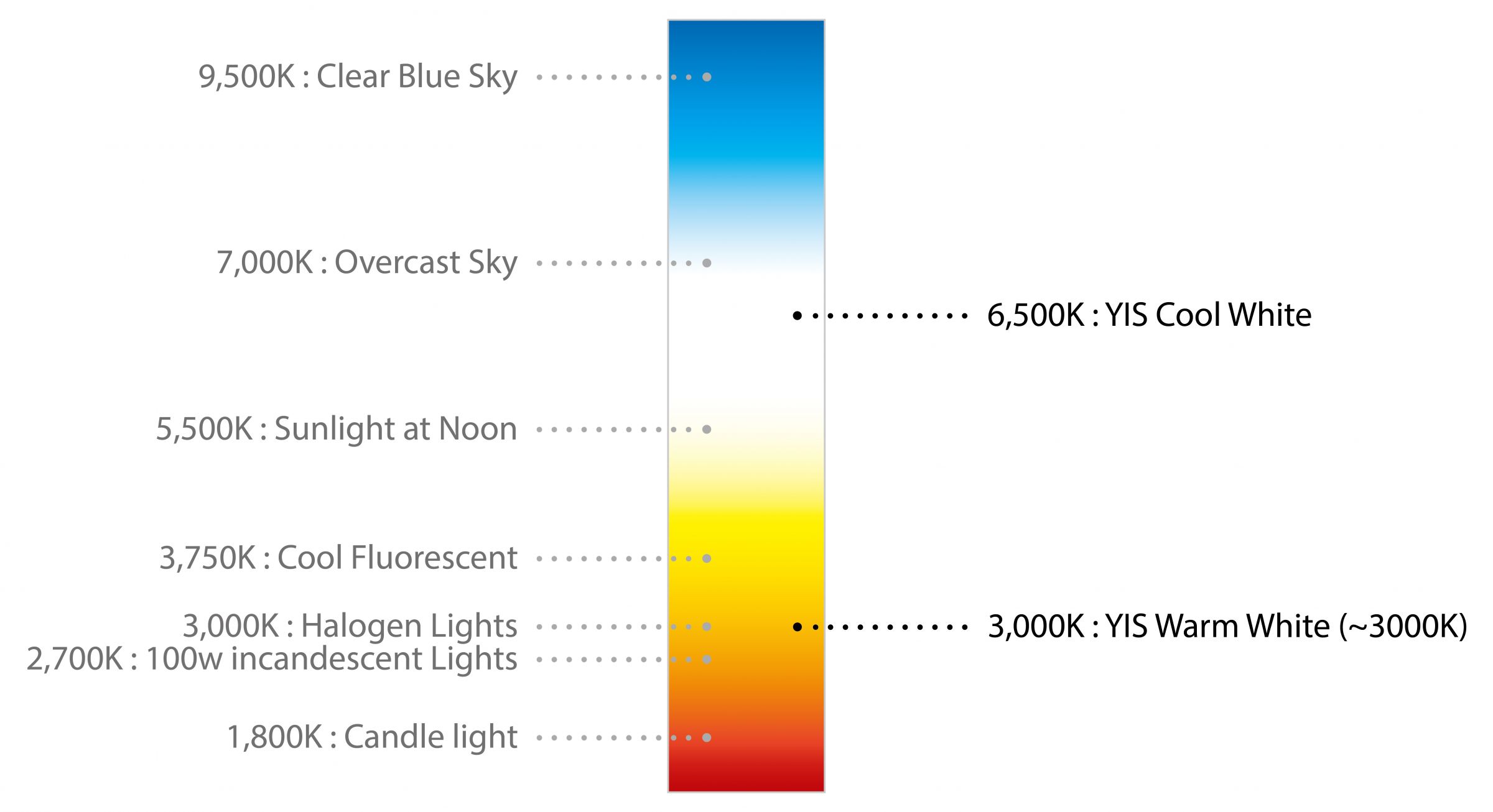
Luminous Flux (Unit: lm(lumens) )
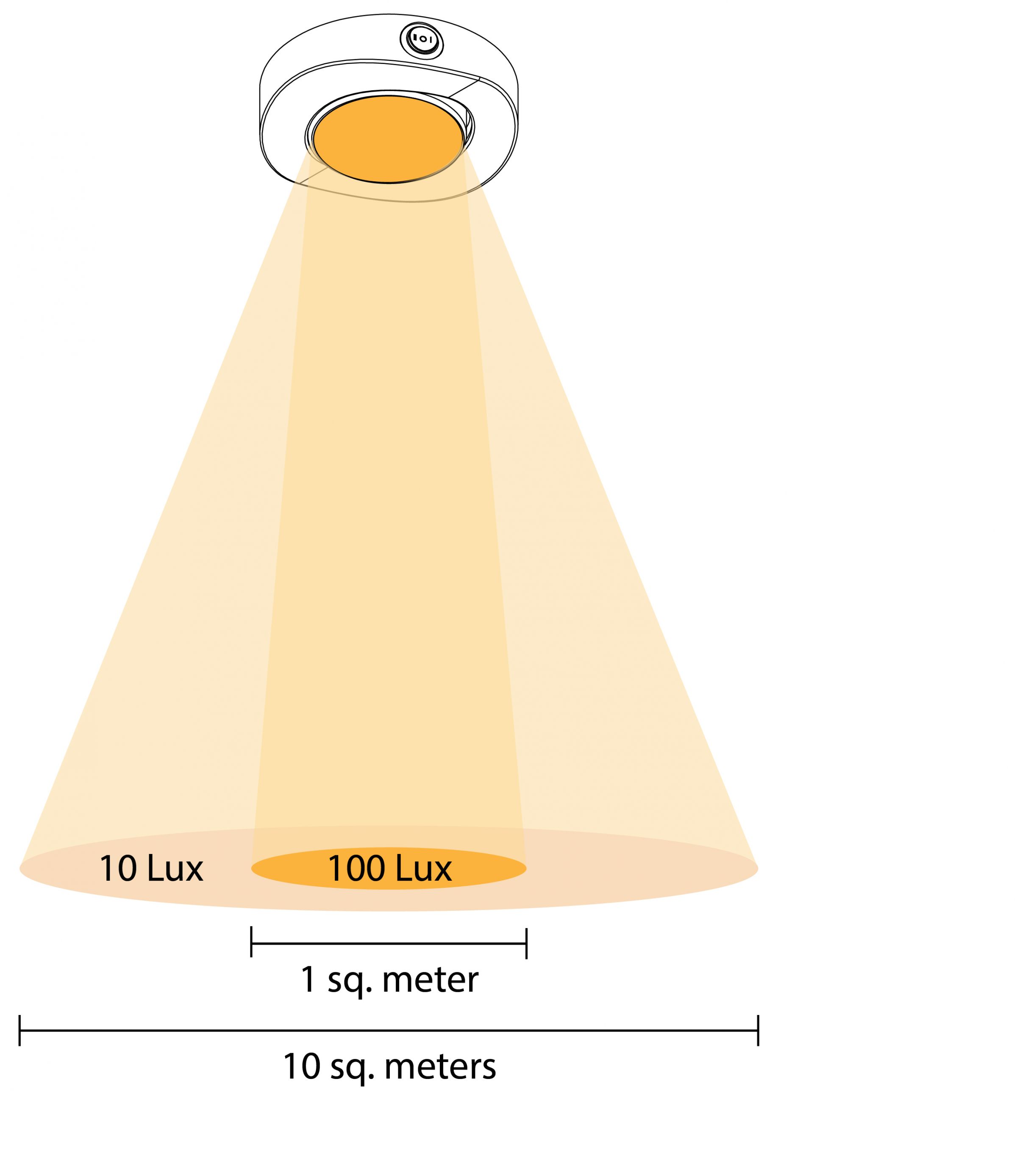
The total amount of light emitted from a lamp. The higher lumen is, the more intense the light output. Luminous Flux does NOT vary with distances. Normally the lumen reflects the capability of lighting a light fixture is able to provide – the lighter the lumens are the brighter the light fixture is.Illuminance (Unit: Lux )
Illuminance is the total luminous flux falling on a surface. It shows the intensity of the incident light. Mathematically, Illuminance (Lux) = Lumens (lm) / area(m^2) where area is the illuminated area of the light source. The farther the surface are away from the source, the larger the area would be, and hence the smaller illuminance, while the Luminous Flux remains the same.Example:
If a light fixture with 100 lumens lights up an area of 1 square meter, the Illuminance would be 100 lux. If, however, the same fixture lights up 10 square meters (at a farther place), the illuminance would be reduced to only 10 lux.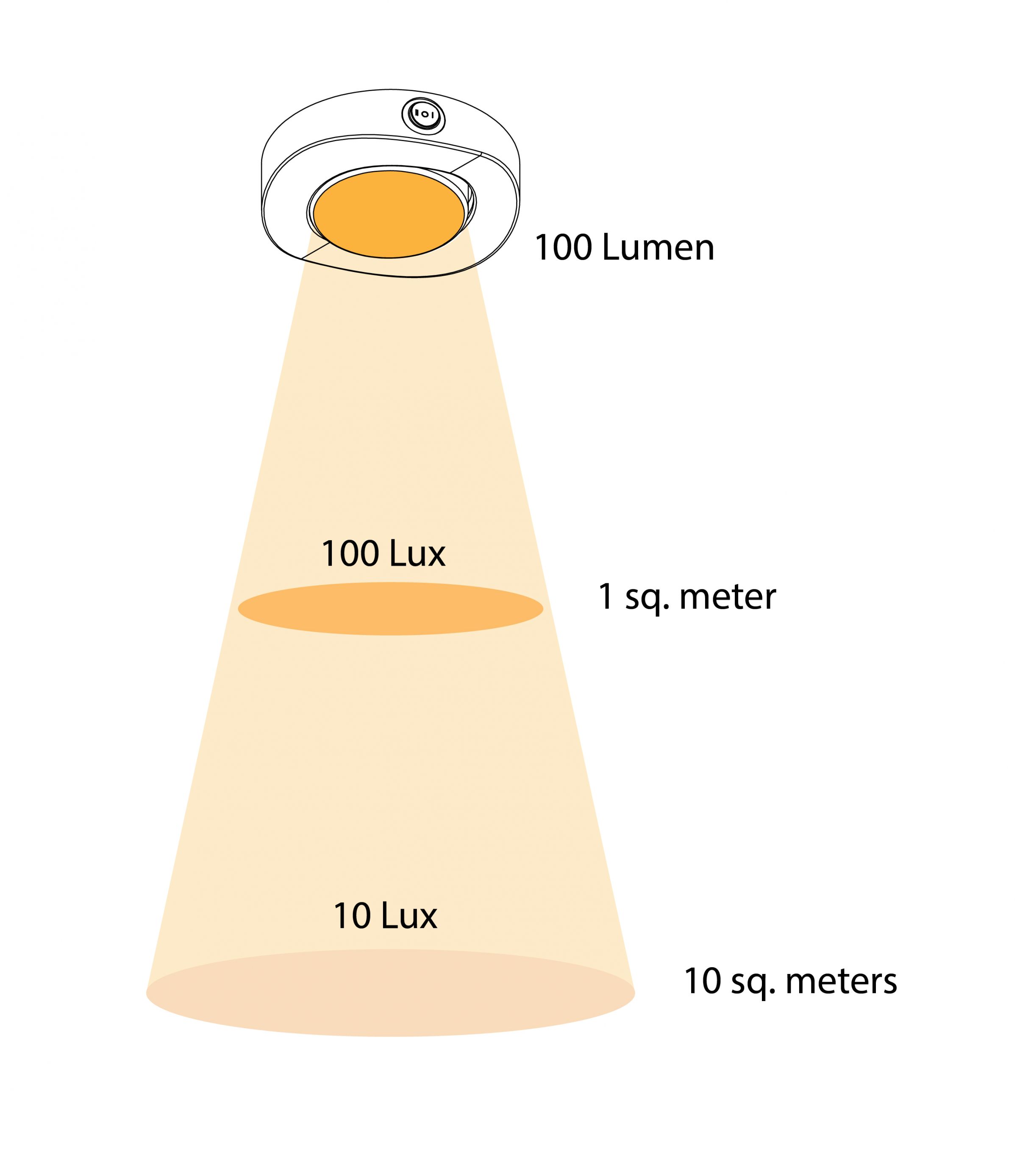
- Related Products
WaveLED Ceiling Light
LC003-3x1W
Wave LED ceiling light with 3x 1W super bright high power LED and built-in ON/OFF switch, adjustable...
DetailsWaveLED Ceiling Light
LC004W
LC004W-W (White) LC004W-S (Matte Silver)LC004 is a unique wave-shaped ceiling light with...
DetailsWaveLED Ceiling Light
LC004WB / LC004WR
Unique wave-shaped ceiling light with built-in switch and tiltable light angle. Using 6 quality...
DetailsCeiling Light with Touch Button
LC005-95
DishLED dimmable ceiling light with touch button in Ø95mm, and linear (non-step) dimming allows...
DetailsCeiling Light with Touch Button
LC005-150
DishLED dimmable ceiling light with touch button in Ø150mm, and linear (non-step) dimming...
Details